Computer Viruses and Malware
Computer malware is a term that comprises harmful computer programs, or less dangerous applications that computer users commonly try to avoid installing. Such programs seek to initiate certain activities on user’s computer, usually unpleasant and bothersome ones. Most of the malware variants implement illegal activities, for instance, steal personal information, corrupt victim’s files, lock the computer and demand a ransom, and so on. Since these programs are very dangerous, the majority of computer users are aware of them. Ransomware, keyloggers, Trojan horses are well-known terms among PC users; however, there are thousands of less dangerous computer programs that also initiate objectionable activities, for instance, adware, browser hijackers, rogue anti-spyware software, and other potentially unwanted programs.
Typically, unwanted computer programs seek to find a way to slither into user’s computer system unnoticed. To achieve this goal, their developers utilize various tricky distribution techniques. Users who strive to install pirated versions of software can easily end up installing malware because cyber criminals frequently attach malicious files to software cracks. It is also strongly advisable to avoid entering websites that are suspected of phishing or malware. If your browser warns you that the website ahead is dangerous, do not enter it. What is more, it is a well-known fact that malware spreads via malvertising (malicious advertising), a method that can help to infect computers pre-click and post-click. Malicious advertisements can be injected into legitimate websites or ad networks. Finally, malicious programs are distributed via email attachments as well. To execute malware, it is enough to download and open a malicious email attachment, which initially seemed like a harmless file. Cyber criminals create new malware distribution techniques each year, and the most efficient way to protect your computer from cyber attacks is to protect the computer with anti-malware software.
Different viruses function differently. The majority of malicious programs are created with an intention to swindle money or sensitive data from computer users, typically by encrypting their files and demanding a ransom, recording victim’s keystrokes, and carrying out other illegal activities. Meanwhile, less dangerous programs like adware or browser hijackers are meant to make changes in user’s computer system, collect personally non-identifiable data, use it for marketing purposes and finally serve targeted advertisements during browsing sessions. Such programs belong to spyware category, and their primary object is to generate pay-per-click revenue for their developers. The family of malware programs is well-known for its ability to slow down computer’s performance, deactivate legitimate security software, display bogus alerts about computer system problems, and run clandestine activities without being detected. However, the owner of an infected computer can realise that computer is affected by malware from particular signs, for example, an appearance of annoying pop-up messages, unexpected changes in system settings, system slowdowns, browser redirects, inaccessible files and the like.
If you suspect that your computer has been infected, it is strongly advisable to run a system scan with a reputable malware removal program. If the PC has been endangered by a powerful malware, you might have to reboot your computer into Safe Mode first. A full system scan with a good anti-malware software reveals all dangerous files and programs on your computer and allows to delete them all at once. If you do not have a computer protection software yet, please navigate to Software page and select the program that seems the best to you. However, if you know what computer parasite is running on your system, you can search our malware database and find individual removal guides for each of them. Some computer parasites can be removed manually rather easily.
Latest Viruses Added to the Database
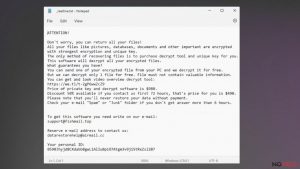
Steps for removing Bozq ransomware
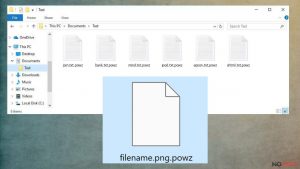
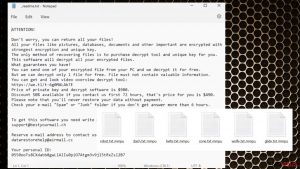
Uninstalling Powz ransomware
Mmpu ransomware removal tutorial
Additional information added on 2016-08-18